-
July, 26,2025
Understanding the Role of Bloom Strength in Soft Gelatin Capsules
-
July, 25,2025
Bloom Strength and Its Impact on Hard Gelatin Capsules
-
July, 21,2025
How Gelatin Is Revolutionizing Pet Food: A Healthier Option for Dogs
-
June, 22,2025
Collagen as a Trusted Ingredient: Meeting Global Demand with Reliable Supply
Gelatin as a Pharma Excipient: Uses and Pros
Gelatin as a pharmaceutical excipient has been a trusted ally in drug formulation for centuries, shaping how we take everything from daily vitamins to life-saving medications. But what makes this collagen-derived protein so special—and where does it fall short?
Whether you’re a researcher, formulator, or manufacturer, understanding gelatin’s role in pharmaceuticals is key to unlocking its potential or finding the right alternative. This article dives into its properties, applications, benefits, and challenges, offering practical insights to help you decide if gelatin is the excipient your project needs.

Introduction to Gelatin in Pharmaceuticals
What Is Pharmaceutical Excipient?
Pharmaceutical excipients are inactive ingredients added to drug formulations to enhance their performance, stability, or delivery. Unlike active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) that provide therapeutic effects, excipients serve as the backbone of a medication—acting as fillers, binders, coatings, or carriers. They ensure the drug is palatable, stable, and effectively delivered to the body.
Gelatin, a natural protein derived from collagen, stands out as one of the most widely used excipients due to its versatility and compatibility with human physiology. Whether you’re swallowing a capsule or chewing a coated tablet, chances are gelatin played a role in getting that medicine to you.
Why Gelatin? A Historical Perspective
Gelatin’s journey in pharmaceuticals dates back centuries, with its origins tied to food and medicinal practices. By the 19th century, pharmacists recognized its potential to encase bitter powders in digestible shells—leading to the invention of gelatin capsules. This innovation revolutionized drug delivery, making medications easier to administer and more patient-friendly.
Over time, gelatin evolved from a simple capsule material to a multifunctional excipient, prized for its ability to gel, stabilize, and protect sensitive ingredients. Its long-standing use reflects a blend of tradition and science, cementing its place in modern pharmaceutical manufacturing.

Overview of Gelatin’s Role Today
Today, gelatin is a cornerstone of pharmaceutical formulations, appearing in everything from over-the-counter painkillers to advanced biologics. It’s most famous for forming the shells of hard and soft capsules, but its role extends to tablet coatings, emulsions, and even wound dressings.
Derived primarily from bovine or porcine sources, gelatin meets stringent quality standards to ensure safety and efficacy. Its natural abundance and adaptability make it a go-to choice for manufacturers, while ongoing research continues to explore its potential in cutting-edge drug delivery systems. Understanding gelatin’s modern applications sets the stage for appreciating its unique properties and challenges.
Properties of Gelatin That Make It an Ideal Excipient
Physical and Chemical Characteristics
Gelatin’s appeal as a pharmaceutical excipient starts with its unique physical and chemical traits. Derived from collagen through hydrolysis, it’s a protein that forms a gel when mixed with water—a property that’s key to creating capsule shells and stabilizing emulsions. It’s soluble in hot water but sets into a firm, flexible matrix as it cools, making it ideal for encapsulating both solid and liquid drugs.
Chemically, gelatin is stable across a range of pH levels, though it can degrade under extreme conditions like high heat or acidity. Its film-forming ability also shines in tablet coatings, providing a smooth, protective layer that enhances shelf life and swallowability.
·Gelling Ability: Forms a gel with water, ideal for capsule shells.
·Solubility: Dissolves in hot water, sets as it cools for flexible matrices.
·Film-Forming: Creates smooth, protective tablet coatings.
·Stability: Holds up across a range of pH levels, though sensitive to extremes.
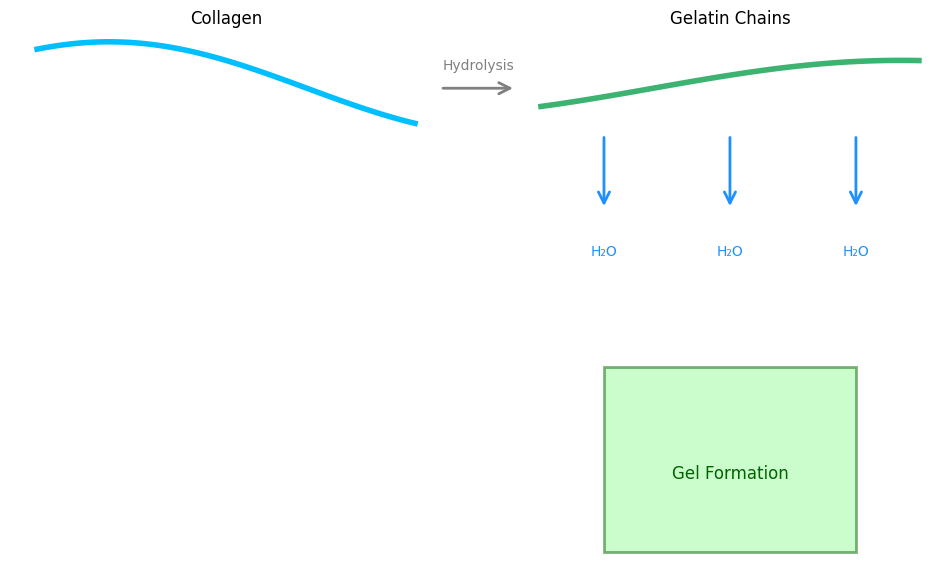
How gelatin’s structure enables its pharmaceutical versatility
As a leading gelatin manufacturer, Funingpu harnesses these traits to produce high-quality gelatin tailored for pharmaceutical use, ensuring consistency in viscosity and gel strength.
Biocompatibility and Safety Profile
One of gelatin’s biggest strengths is its biocompatibility. Since it’s derived from animal collagen—similar to what’s found in human tissues—it’s naturally well-tolerated by the body. This makes it a safe choice for oral, topical, and even injectable formulations. Gelatin is digestible, breaking down into amino acids in the stomach, which minimizes the risk of adverse reactions.
While rare allergies (e.g., to bovine or porcine sources) can occur, pharmaceutical-grade gelatin undergoes rigorous purification to remove impurities, aligning with safety standards like those set by the FDA and USP. For patients and manufacturers alike, this safety profile is a major draw.
Versatility Across Formulations
Gelatin’s adaptability sets it apart from many synthetic excipients. It can be molded into hard capsules for dry powders, softened with plasticizers for chewy softgels, or blended into tablets as a binder. Its gelling properties also support controlled-release formulations, where drugs need to dissolve gradually.
Beyond solids, gelatin stabilizes suspensions and emulsions, ensuring uniform drug distribution. This flexibility allows formulators to tweak its concentration or processing to suit diverse needs—whether it’s a fast-dissolving vitamin or a slow-release painkiller. For pharmaceutical innovators, gelatin’s multifunctionality is a toolkit in itself.
Sourcing: Bovine vs. Porcine Gelatin
Gelatin’s properties can vary depending on its source, with bovine (cow) and porcine (pig) origins being the most common. Bovine gelatin often has a higher gel strength, making it a favorite for firm capsule shells, while porcine gelatin may offer better clarity and flexibility, ideal for softgels.
The choice impacts not just performance but also cultural or dietary considerations—porcine gelatin, for instance, may not suit halal or kosher markets. Both types are processed to meet pharmaceutical-grade purity, but sourcing affects cost and availability too. Understanding these differences helps formulators pick the right gelatin for their specific application.
Key Applications of Gelatin in Drug Delivery Systems
Hard and Soft Gelatin Capsules
Gelatin’s most iconic role in pharmaceuticals is in capsule manufacturing. Hard gelatin capsules, typically two-piece shells, are perfect for encasing dry powders or granules—like antibiotics or supplements. They’re made by dipping molds into a hot gelatin solution, which cools into a sturdy, digestible casing that dissolves in the stomach.
Soft gelatin capsules, or softgels, take it a step further by blending gelatin with plasticizers like glycerin, creating a flexible shell for oils, liquids, or pastes—think fish oil or vitamin E. Both types leverage gelatin’s film-forming and gelling properties, offering a reliable, patient-friendly way to deliver precise doses.
Funingpu gelatin, known for its pharmaceutical grade gelatin, excels in this application, offering reliable, digestible shells that meet stringent industry standards


Gelatin as a Tablet Binder and Coating Agent
Beyond capsules, gelatin plays a supporting role in tablets. As a binder, it helps powders stick together during compression, ensuring tablets hold their shape without crumbling. Even small amounts of gelatin can improve cohesion, making it a cost-effective additive. As a coating agent, gelatin forms a thin, glossy layer around tablets, masking bitter tastes, protecting active ingredients from air or moisture, and easing swallowing.
This dual functionality makes it a staple in solid dosage forms, especially for over-the-counter meds where patient experience matters as much as efficacy.

Controlled-Release Formulations
Gelatin shines in controlled-release systems, where drugs need to be released gradually rather than all at once. Its gelling properties allow formulators to create matrices or coatings that slow dissolution—ideal for painkillers or chronic disease treatments. Cross-linked gelatin, treated to resist immediate breakdown, can extend release times even further, while gelatin microspheres offer precision in targeted delivery.
This adaptability helps manage drug bioavailability, reducing side effects and improving compliance. For scientists tackling complex release profiles, gelatin provides a natural, tweakable solution.
Emerging Uses in Advanced Therapies
Gelatin’s role is evolving beyond traditional drugs into cutting-edge applications. In biologics, it stabilizes vaccines or proteins that might degrade without protection. It’s also used in wound dressings and tissue engineering, where its biocompatibility supports cell growth or healing.
Researchers are exploring gelatin nanoparticles for delivering genes or cancer drugs directly to cells, capitalizing on its ability to form tiny, drug-loaded carriers. These innovations highlight gelatin’s potential as a bridge between conventional pharmaceuticals and next-gen therapies, making it a material to watch in the lab and clinic.
Benefits and Challenges of Using Gelatin as an Excipient
Advantages of Gelatin in Formulations
Gelatin brings a host of benefits to pharmaceutical formulations. It’s cost-effective, widely available, and easy to process, making it a favorite for manufacturers scaling up production. Its natural origin and digestibility appeal to patients, while its versatility—spanning capsules, coatings, and more—saves formulators from juggling multiple excipients.
Gelatin also excels at masking unpleasant tastes or odors, improving the user experience for oral drugs. Plus, its ability to form clear, strong films ensures product stability and a professional look on the shelf. For budget-conscious companies and patient-focused designs, gelatin is tough to beat.

Limitations: Stability and Environmental Factors
Despite its strengths, gelatin has quirks that can trip up formulators. It’s sensitive to moisture, softening or dissolving if exposed to high humidity, which can shorten shelf life or ruin capsules in tropical climates. Heat is another foe—gelatin melts above 35–40°C, limiting its use with heat-sensitive drugs or in hot manufacturing processes.
Its stability also falters in highly acidic or alkaline conditions, risking degradation. These environmental vulnerabilities mean extra care in storage, packaging, or formulation tweaks—like adding stabilizers—is often needed to keep gelatin-based products intact.
Addressing Allergenicity and Dietary Restrictions
Gelatin’s animal-derived nature (typically bovine or porcine) raises red flags for some. Though rare, allergies to gelatin can occur, posing risks in vaccines or capsules for sensitive patients. More commonly, dietary or religious preferences—like vegetarian, vegan, halal, or kosher diets—clash with its sourcing, shrinking its market in diverse populations.
Manufacturers can mitigate this by clearly labeling origins or exploring fish-derived gelatin, but these alternatives often cost more or lack the same performance. For formulators, balancing patient inclusivity with gelatin’s benefits is a persistent challenge.
Regulatory Compliance and Quality Standards
Gelatin’s use in pharmaceuticals isn’t a free-for-all—it must meet strict regulatory benchmarks. The FDA and USP set guidelines for purity, ensuring it’s free of contaminants like heavy metals or pathogens (e.g., BSE from bovine sources). Pharmacopeial standards also dictate gel strength, viscosity, and microbial limits, so every batch must be tested rigorously.
Compliance adds cost and complexity, especially for global markets with varying rules. Yet, these standards reassure users of gelatin’s safety and consistency, making it a trusted choice when quality control is airtight.
Among pharmaceutical gelatin manufacturers, Funingpu stands out by adhering to these standards, delivering certified, high-purity gelatin for safe formulations.
Practical Solutions and Alternatives to Gelatin
Overcoming Stability Issues
Gelatin’s sensitivity to moisture, heat, and pH can be a hurdle, but smart strategies can keep it in play. To tackle humidity, manufacturers can use desiccant packets or moisture-resistant packaging like blister packs, preserving capsule integrity in damp climates. For heat concerns, adjusting production to lower temperatures or adding stabilizers like glycerol can prevent melting during processing. pH instability?
Buffering agents in the formulation can maintain a neutral range, protecting gelatin from breakdown. These tweaks let formulators harness gelatin’s benefits without compromising product quality, even in challenging conditions.

Vegetarian and Vegan Excipient Options
For patients or markets rejecting animal-derived gelatin, plant-based alternatives are gaining traction. Hydroxypropyl methylcellulose (HPMC) is a top contender, forming robust capsule shells that mimic gelatin’s performance—minus the dietary restrictions. Pullulan, a polysaccharide from fungi, offers another vegan option with excellent oxygen barrier properties, ideal for sensitive drugs.
Carrageenan and pectin can also step in, though they’re less common. While these substitutes often cost more and may lack gelatin’s gelling versatility, they open doors to vegetarian, vegan, halal, and kosher consumers, making them worth considering for inclusive formulations.
Innovations in Gelatin Processing
Science is pushing gelatin itself forward, sidestepping some of its natural flaws. Cross-linking gelatin with agents like glutaraldehyde strengthens it, boosting resistance to heat and enzymes for longer-lasting controlled-release drugs. Recombinant gelatin, produced via microbial fermentation, ditches animal sourcing altogether—offering a consistent, allergen-free alternative that’s still in gelatin’s family.
Fish-derived gelatin is another twist, appealing to some dietary niches while maintaining traditional properties. These innovations keep gelatin relevant, blending its classic strengths with modern demands for sustainability and performance.
Sourcing and Supply Chain Considerations
Choosing the right gelatin starts with sourcing. Bovine and porcine gelatin dominate, but quality varies—look for suppliers with USP or ISO certifications to ensure purity and traceability.
Regional availability matters too; porcine gelatin might be cheaper in Europe, while bovine rules in North America. For dietary-sensitive markets, exploring fish or recombinant options can dodge supply chain snags tied to cultural bans. Building relationships with reliable vendors and testing batches for gel strength or contaminants keeps production smooth. A strategic supply chain turns gelatin from a commodity into a tailored asset for your formulation.
As a gelatin manufacturer with over 30 years of experience, Funingpu offers certified pharmaceutical grade gelatin from its advanced production base, ensuring reliability for global supply chains.
Is Gelatin Right for Your Pharmaceutical Needs?
Weighing the Pros and Cons
Gelatin’s place in pharmaceuticals is a balancing act of strengths and trade-offs. On the plus side, its affordability, versatility, and patient-friendly nature make it a workhorse for capsules, tablets, and beyond. It’s a natural fit for manufacturers seeking reliable, scalable solutions. Yet, its sensitivity to moisture and heat, plus dietary or allergenic concerns, can complicate things—especially for global or niche markets.
If stability and inclusivity are non-negotiable, alternatives like HPMC might edge it out. For many, though, gelatin’s benefits outweigh its quirks, especially with the right formulation tweaks or sourcing strategy in place.
Future Trends in Gelatin Use
Gelatin’s story isn’t static—it’s evolving with industry shifts. Demand for sustainable, animal-free options is driving recombinant gelatin into the spotlight, promising a future where dietary restrictions don’t limit its reach. Advances in cross-linking and nanotechnology could expand its role in precision drug delivery, from cancer therapies to personalized medicine.
Meanwhile, regulatory scrutiny on sourcing (think BSE or ethical concerns) will keep pushing quality standards higher. As pharmaceuticals lean toward innovation and inclusivity, gelatin’s adaptability suggests it’ll stay relevant, reinventing itself for tomorrow’s challenges.
Next Steps for Researchers and Manufacturers
So, where do you go from here? If you’re a researcher, dig into gelatin’s emerging applications—test cross-linked variants or nanoparticles for your next project. Manufacturers might audit their supply chain, locking in high-quality gelatin or trialing plant-based substitutes to broaden appeal.
Either way, consult with formulation experts or regulatory bodies to nail down specifics, from stability testing to compliance. Gelatin’s a tool with proven power, but its success hinges on tailoring it to your goals. Explore, experiment, and decide—gelatin might just be the excipient your product needs.

Final Thoughts
Gelatin remains a key pharmaceutical excipient, balancing versatility with innovation. From capsules to advanced therapies, its strengths endure. Challenges exist, but solutions ensure its future. Quality suppliers, like Funingpu gelatin, support researchers and manufacturers in meeting modern demands effectively.
Phone: +86-577-88105990
Mobile: +86-138 5886 1938
Official Website: www.fnp-gelatin.com
Email: sales@funingpu.com
Address: No. 1-10 Wenpu Road, Yacheng Town, Xiapu County, Ningde City, Fujian Province




