-
July, 26,2025
Understanding the Role of Bloom Strength in Soft Gelatin Capsules
-
July, 25,2025
Bloom Strength and Its Impact on Hard Gelatin Capsules
-
July, 21,2025
How Gelatin Is Revolutionizing Pet Food: A Healthier Option for Dogs
-
June, 22,2025
Collagen as a Trusted Ingredient: Meeting Global Demand with Reliable Supply
Gelatin vs. Collagen—What Every Manufacturer Needs to Know
Gelatin and collagen are two key functional raw materials in the food, pharmaceutical and beauty industries. Although they are both derived from animal collagen, there are significant differences in the production process, physical properties and application areas. This article will delve into the differences between the two and provide key insights for manufacturers when choosing the right raw material for their products.
Understand Gelatin and Collagen
Gelatin
After reading the above explanation of collagen, it is not difficult to understand that gelatin is a protein product obtained after partial hydrolysis of natural animal collagen. Simply put, it is a deep-processed product of natural collagen. It is usually taken from the skin, bones and other connective tissues of animals. Due to the deep processing of hydrolysis, gelatin, a hydrophilic macromolecular colloid, has many unique properties and is widely used in various production fields.
Collagen
Collagen is a biological polymer that naturally exists in the skin, bones and connective tissues of mammals. Compared with the protein in the human body, collagen accounts for 25%~30% of the total protein content, providing structural support for various tissues to ensure their elasticity and toughness. Commercial customized collagen is usually extracted from the skin, bones and other connective tissues of animals, and is widely used in food, medicine and health care, cosmetics and other fields.

Source of raw materials
The following are the sources of gelatin and collagen:
· Mammals: The most common source of collagen, such as cowhide, pig skin, etc.
· Fish: Including fish skin, fish scales and some marine organisms, such as fish skin gelatin.
· Poultry: For example, chicken skin and chicken bones can also be used as sources of collagen.
According to the current market situation, gelatin and collagen usually come from animal skin, bones and other connective tissues. The more common raw materials are pig skin, cowhide, etc. Cattle and pigs are currently the important sources of gelatin and collagen on the market.
Key Differences Between Gelatin and Collagen
Production Processes
|
Production Processes |
Collagen |
Gelatin |
|
Pre-treatment |
After the raw materials have been cleaned and physically treated, collagen extraction proceeds directly. The pre-treatment stage usually does not involve strong chemical treatments in order to preserve the triple helix structure of collagen. |
In the pre-treatment stage of gelatin production, the raw materials are generally treated with acid or alkali, which softens the tissue and helps break down collagen, making gelatin easier to hydrolyze. How long this step lasts depends on the desired gelatin properties. |
|
Extraction |
Collagen extraction is usually carried out under mild conditions, using enzymatic hydrolysis or acid-base treatment, with the goal of preserving the natural structure of collagen as much as possible. Extracted collagen can be further processed into hydrolyzed collagen (collagen peptides), which is more easily absorbed by the human body. |
When gelatin is extracted, it needs to be done in hot water. The collagen in the raw material will be hydrolyzed during the heating process, causing the helical structure of collagen to unwind and further decompose into smaller polypeptide chains, forming gelatin that is soluble in hot water. This process is usually carried out at a higher temperature to ensure sufficient hydrolysis. |
|
Purification |
After extraction, collagen usually goes through a series of filtration, centrifugation and drying steps to remove impurities and obtain purified collagen powder. These steps are carried out at low temperatures to avoid destroying the triple helix structure of collagen. |
The extracted gelatin solution is filtered and degassed before being concentrated and dried. The drying process of gelatin is usually carried out by spray drying or drum drying to form gelatin flakes, powder or granules. |
From the perspective of the main production process, the extraction process of gelatin usually requires higher temperatures and specific chemical treatments to break down collagen into polypeptide chains; while the collagen production process focuses more on extraction under mild conditions to protect its natural triple helix structure. This significant difference leads to different applications in their final uses and product forms.
Physical properties
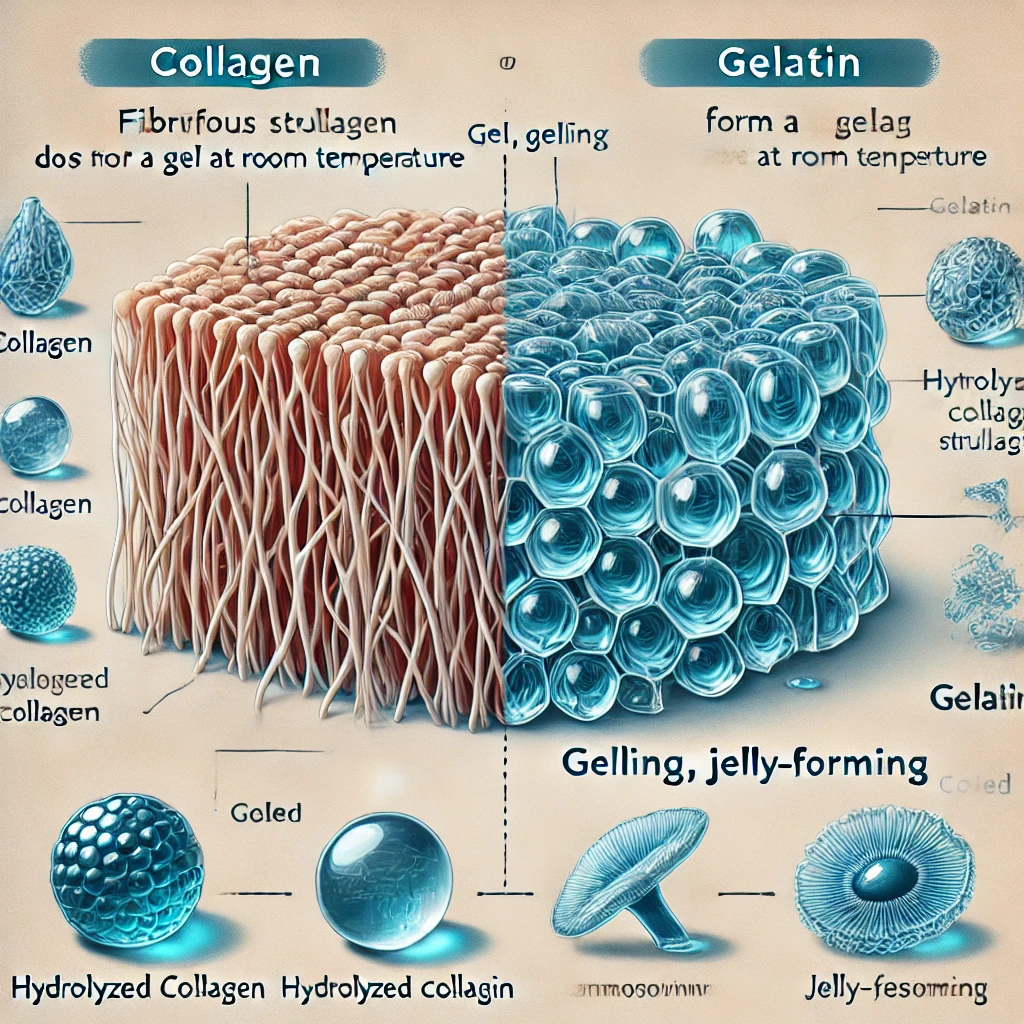
· Collagen: It maintains its original fibrous structure and usually does not form a gel at room temperature. Hydrolyzed collagen (collagen peptide) is a small molecule structure, easily soluble in water, and has no gelling properties. Collagen is not easily soluble in water, but can be made into hydrolyzed collagen or collagen peptides through enzymatic hydrolysis or acid-base treatment. The latter is easily soluble in water and more easily absorbed by the human body.
· Gelatin: It has unique gelling properties and can form a jelly after being dissolved in hot water and cooled. The gel strength and melting point of gelatin can be adjusted by controlling the production conditions, which makes it very useful in the food and pharmaceutical industries. Gelatin is easily soluble in hot water and can form a gel when cooled, so it is often used as a thickener, stabilizer and gelling agent in food, medicine and cosmetics.
Functions and Applications
Gelatin is used as a thickener, stabilizer and gelling agent in the food industry, such as in jellies, candies, ice cream and some dairy products; in the pharmaceutical field, it is used to make coatings for medicinal capsules and tablets, etc., because it is edible and has good biocompatibility. Therefore, the main function of gelatin lies in its physical properties, such as thickening, gel formation and stabilizer.
Collagen is used in health products to support skin health, joint function and bone strength because it can provide structural support and promote tissue repair in the body; in beauty products, collagen is widely used in skin care products for its anti-aging and moisturizing effects. Collagen has a wider range of health benefits, such as improving skin elasticity, promoting joint health, and enhancing bone density. Collagen supplements are widely promoted in the market as anti-aging and bone health support products.
Gelatin is more regarded as a functional ingredient rather than a bioactive ingredient because its triple helix structure is destroyed during its production process. The triple helix structure retained by collagen during the production process gives it good biocompatibility and functionality. It is widely used in health products, skin care products, medical materials and functional foods, therefore placing more emphasis on its biological functions.
Key Insights for Manufacturers Choosing Between Gelatin and Collagen
Manufacturers need to consider the following key factors when choosing gelatin or collagen:
Application Product Requirements
In the field of health and beauty, if the goal is to provide health supplements, skin care products or anti-aging products, collagen (especially hydrolyzed collagen) is more suitable because it can effectively improve skin elasticity, improve joint health, and is more easily absorbed by the body. In terms of medical applications, the biocompatibility and activity of collagen are very important when used for medical purposes such as tissue repair and wound healing.
Gelatin:As a thickener, gelling agent and stabilizer in food, the gelling properties of gelatin are key, especially in products such as candy, jelly, yogurt, etc. For pharmaceutical industries such as pharmaceutical capsules and drug formulations, the purity, solubility and stability of gelatin are important considerations.
Product Features
Collagen:
Bioactivity: When choosing collagen, you need to pay attention to whether it retains the triple helix structure (especially hydrolyzed collagen) to ensure its bioactivity. Funingpu’s collagen peptides are carefully processed to maintain their structural integrity and high absorption efficiency, making them perfect for products that require fast and effective health benefits.
Solubility and absorbability: Hydrolyzed collagen (collagen peptides) has a high absorption efficiency in the body and is suitable for products that need to take effect quickly.
Gelatin:
Gelating properties: The gelling temperature, solubility and gelatin concentration of gelatin are key parameters that affect its performance in food and pharmaceutical applications.
Drying and processing: The form of gelatin (flakes, powder) and its drying method also affect the use effect of the product.
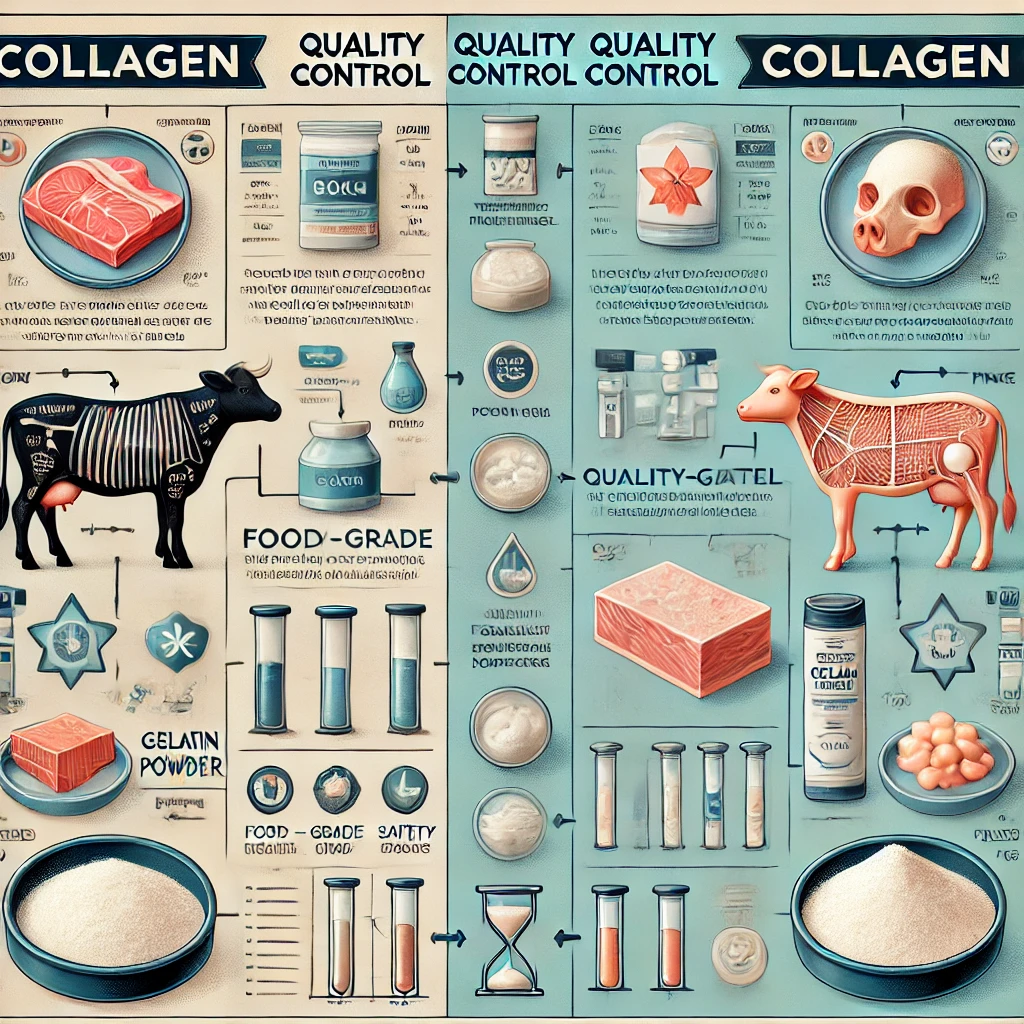
Source and Quality
The source and quality of gelatin and collagen are key factors that influence their functionality and suitability for specific applications. Funingpu Gelatin places a strong emphasis on the traceability of its raw materials, ensuring that our products meet the highest standards of food and drug safety. Our dedication to transparency and rigorous quality control ensures that every batch of gelatin or collagen exceeds industry expectations.
Whether your product requires food-grade or pharmaceutical-grade gelatin, Funingpu is committed to providing solutions that not only meet but often exceed the industry's top regulatory and quality standards. As a member of the China Gelatin Association, we ensure that our production processes adhere to strict quality control measures, offering peace of mind for manufacturers seeking top-tier raw materials.
Final Thoughts
Gelatin and collagen each have unique characteristics and application advantages. Choosing the right material depends on the specific needs of the product and market positioning. By understanding the production process, physical properties and application scenarios of both, manufacturers can make more informed decisions to enhance the competitiveness of their products. In the face of growing market demand, choosing the right raw materials can not only improve product quality, but also meet consumers' pursuit of health and functionality.
FAQ
1. What’s the main difference between gelatin and collagen?
Gelatin is a hydrolyzed form of collagen used mainly for its gelling properties, while collagen is a structural protein used for its health benefits.
2. Where are gelatin and collagen sourced from?
Both are typically derived from animal skins, bones, and connective tissues. Collagen can also come from fish.
3. What should manufacturers consider when choosing between gelatin and collagen?
Consider the product’s functional requirements, physical properties, and source quality.
4. Can gelatin and collagen be used interchangeably?
Not always. Gelatin is best for gelling, while collagen is used for health benefits. The choice depends on the product’s purpose.
Phone: +86-577-88105990
Mobile: +86-138 5886 1938
Official Website: www.fnp-gelatin.com
Email: sales@funingpu.com
Address: No. 1-10 Wenpu Road, Yacheng Town, Xiapu County, Ningde City, Fujian Province




