-
July, 26,2025
Understanding the Role of Bloom Strength in Soft Gelatin Capsules
-
July, 25,2025
Bloom Strength and Its Impact on Hard Gelatin Capsules
-
July, 21,2025
How Gelatin Is Revolutionizing Pet Food: A Healthier Option for Dogs
-
June, 22,2025
Collagen as a Trusted Ingredient: Meeting Global Demand with Reliable Supply
Pectin vs. Gelatin: Choosing the Right Gelling Agent for Food and Pharmaceutical Manufacturing
When it comes to selecting the ideal gelling agent for food and pharmaceutical products, pectin vs. gelatin is a common comparison, as both are popular options with distinct properties. Each offers unique characteristics that impact the texture, stability, nutritional profile, and functionality of the end product. This article delves into the differences between pectin and gelatin, exploring their specific properties, applications in food and pharmaceutical manufacturing, and key factors to consider when deciding between the two.
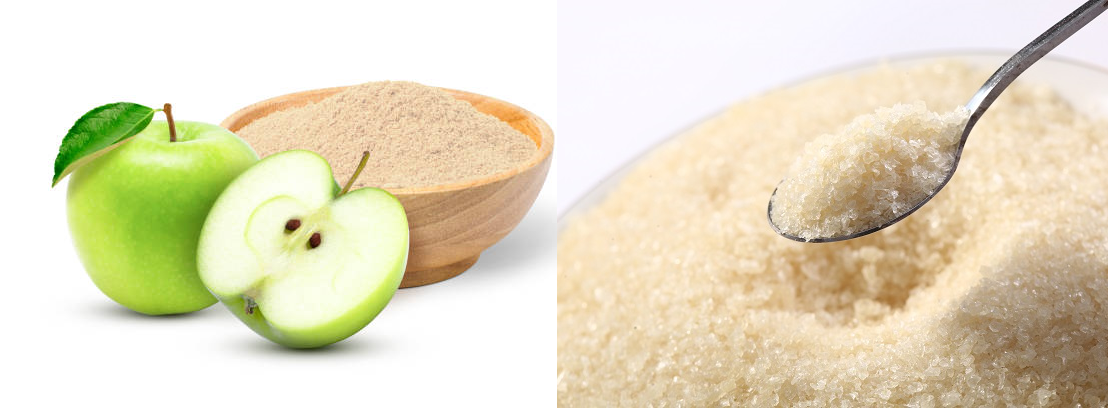

Is Pectin the Same as Gelatin
Pectin and gelatin are both gelling agents used throughout several industries. However, they are fundamentally different in their origin, properties, and applications.
Pectin vs. Gelatin: Source
Pectin is a naturally occurring fiber that is predominantly extracted from the cell walls of fruits, such as apples and citrus fruits. It is plant-based; hence, it is ideal for vegan and vegetarian products.
Gelatin, on the other hand, is a protein derived from animal collagen, usually extracted from bovine or porcine sources. Gelatin manufacturers often produce various types, including pharmaceutical grade gelatin for drug delivery and edible gelatin for food applications. Because of its animal-based origin, gelatin is typically unsuitable for vegan or vegetarian products but compatible for use in certain food and pharmaceutical products.

Funingpu’s pharmaceutical grade gelatin is sourced from high-quality bovine and porcine collagen, ensuring both purity and safety in every batch. This level of quality control supports the specialized demands of pharmaceutical applications, where consistent, reliable ingredients are crucial.
Pectin vs. Gelatin: Texture and Gel Formation
Pectin and gelatin remain quite contrasting in their texture or gel formation; thus, this affects the mouthfeel and stability of the final product.
·Gelatin Texture: Gelatin gives a soft, smooth, and flexible gel that melts in the mouth. It is this characteristic feature that draws its use in products where a creamy or jiggly texture is required, such as marshmallows, gummy candies, and mousses. Gelatin powder wholesale is popular in the food industry for creating these textures efficiently and at scale.
·Pectin Gel Texture: In contrast to it, pectin sets as a stiffer more brittle gel. This texture is often desired in applications such as spreads, jams, and jellies, where the desirable texture is often firm enough to be sliced.

Pectin vs. Gelatin: Temperature and Stability
The demands of temperature and stability on pectin and gelatin also contribute to their application in various fields.
·Gelatin: This gelates at low temperatures and is commonly stable in a cool environment; it is much less tolerant to higher temperatures, melting above 30°C, which justifies why most gelatinous products must be refrigerated. In applications where a melt-in-the-mouth effect or refrigeration is required, it is generally the material of choice.
·Pectin: In contrast, pectin is heat-stable and may withstand higher temperatures. Its gel forms in the presence of acid and sugar, thus it finds an appropriate application in cooking procedures involving high temperatures. Gels from pectin maintain their structures under warm temperatures better than starch-based gels and, therefore suitability in room-temperature-stable products such as jams and fruit-based spreads.
Pectin vs. Gelatin: Nutritional Implication
Owing to the great difference in their composition, differences in their nutritional benefits will occur between pectin and gelatin.
·Gelatin: Gelatin is rich in amino acids, including glycine and proline, which may be useful for nourishing joints, skin, and gut health. For this, a very high bioavailability will exist, suggesting that the body should have ease in absorbing its nutrients and utilizing them, thereby adding value to functional foods and dietary supplements.
·Pectin: Pectin is rich in soluble fiber; therefore, it may contribute to encouraging digestion and heart health since the body absorbs cholesterol. It is, therefore, an ingredient used in most supplements of fiber. This allows a developer to produce multiple health-related supplements targeted at vegans and vegetarians, respectively.
Pectin vs. Gelatin Applications in Food Manufacturing
Both pectin and gelatin have different properties; hence, they are more uniquely applicable in specific areas of food applications and processing.
Pectin in Food
Pectin is an adhesive protein highly capable of forming a firm gel under acidic, high-sugar conditions and hence finds very good application in fruit-based products. Common applications in food include:
·Jams and Jellies: because the gelling property especially works in an acid, sugar-rich environment, pectin is the go-to choice for the production of jam, jelly, and preserves.
·Bakery Fillings: The ability of pectin to form a stable gel makes it an ideal place in baked goods, especially where the filling needs to hold its shape, for instance, in fruit tarts and pastry fillings.
·Low-Sugar Foods: Pectin’s gelling properties are activated in the presence of sugar and acid, making it a suitable agent for low-sugar or sugar-free fruit spreads.
Pectin, since it is derived from plants, finds its place in a staple of vegan and vegetarian products in the area of plant-based and vegan food products, such as fruit snacks and desserts made from plants.

Gelatin in Food
Gelatin is favored in a wide range of applications due to its distinctive textural and functional properties, especially where a smooth and elastic texture is required. Applications include:
·Gummy Candies: Gelatin is, for the most part, the standard ingredient in many gummies because of its flexible texture that can make a chewy, soft gel. Gelatin vs. pectin for gummies would be considered one of the key thoughts in candy manufacturing since the pectin used in gummies is much firmer in terms of biting compared to gelatin-based candies.
·Dairy Products: Some dairy-based products featuring a creamy, smooth consistency could be yogurt, panna cotta, and mousse owed by gelatin creating a 'melts-in-the-mouth' effect.
·Marshmallows and Confectionary: Gelatin gives marshmallows that airy, sponge-like feel. As such, manufacturers have no choice but to use the ingredient, as it can give it that exemplary light and fluffy feel.

Funingpu supplies edible gelatin and gelatin powder wholesale specifically formulated for food applications, such as gummy candies, marshmallows, and dairy products. Known for their smooth, elastic textures, Funingpu’s gelatin products enable manufacturers to create high-quality, appealing food items that consumers love.
H2: Pectin vs. Gelatin Applications in Pharmaceutical Manufacturing
Beyond food processing, pectin, and gelatin have served well in pharmaceutical manufacturing-especially when it comes to supplement and drug delivery systems.
Gelatin Capsules
One of the most common pharmaceutical applications of gelatin is in the manufacturing of capsules. Both hard and soft capsules are made with gelatin, which provides a stable, biodegradable, easily digestible matrix for oral medications and supplements. Among the many advantages of gelatin capsules are the following:
·Bioavailability: Gelatin capsules dissolve rapidly in the stomach, making for quick release of the capsule contents.
·The protection of active ingredients: Gelatin capsules act as a barrier to water, hence lengthening the shelf-life of their content and protection against degradative actions.
·Variety in application: They serve in a variety of formulations which include powder, liquid, and oil-based products. Hence, gelatin capsules have found wide applications in pharmaceutical industries.
Funingpu specializes in pharmaceutical grade gelatin ideal for capsule production, offering hard and soft gelatin capsules that meet the strict standards required by the pharmaceutical industry. Funingpu’s high-quality gelatin provides stability, bioavailability, and optimal barrier properties, supporting product integrity and shelf life.
Pectin in Pharmaceuticals
While less frequent than gelatin, pectin also finds application in some pharmaceutical uses, mainly those where plant-derived ingredients are preferred. Due to the high fiber content of pectin and its ability to form a stable gel, it finds usefulness in:
·Controlled-Release Tablets: The gel-forming properties of pectin will help to control the release of active ingredients; hence, it is suitable for use in extended-release tablets.
·Fiber Supplements: Pectin, being a natural source of soluble fiber, often finds its place in fiber supplements that improve digestion and support cardiovascular health.
·Plant-Based Formulation: The surge in demand by consumers for vegan options has recently driven some companies to begin assessing the use of pectin as a biologically derived alternative to gelatin in capsule formulations.
Stability-Shelf Life Comparison
The stability and, correspondingly, the shelf life of a product are very important issues concerning pharmaceutical products; thus, differences between pectin and gelatin may be reflected in the above properties of the products.
·The Capsule Shell: Gelatin capsules usually have a longer shelf life and can provide great stability in dry conditions. Pharmaceutical grade gelatin offers enhanced stability for long-term use in medical applications. However, it is sensitive to humidity, which may cause the softening or deforming of the capsules.
·Pectin-Based Products: Pectin provides good stability at higher temperatures and does not require refrigeration. However, it is generally less robust than gelatin in capsule applications and is typically used in tablets or chewable rather than encapsulated drugs.
Factors to Consider When Choosing Between Pectin and Gelatin
A variety of different factors must be considered when choosing between pectin and gelatin depending on the product goals, dietary requirements, and the intended use.
Product Goals
The nature of the final product's texture, temperature stability, and ingredient requirements will strongly influence the choice of gelling agent.
·Pectin is ideal for products requiring a firm, structured gel that does not melt easily, such as jams, jellies, and some medicinal syrups.
·Gelatin offers a softer, more elastic texture, making it suitable for gummies, confections, and encapsulated pharmaceuticals.
Dietary Restrictions
Each gelling agent's origin further influences the product's suitability for different diets.
·Pectin is suitable for vegan, vegetarian, and halal or kosher-certified products, as it is plant-based.
·Gelatin is usually derived from animal sources like bovine and porcine sources, which will limit use in consumers for religious or ethical reasons. However, it is generally accepted in products intended for health and beauty applications due to its high collagen content.

Final Thoughts
Both pectin and gelatin have advantages that make them valuable in food and pharmaceutical industries. While gelatin offers a unique, elastic texture and high bioavailability for health products, pectin’s plant origin and stability make it ideal for vegan and high-temperature applications. Gelatin manufacturers and gelatin powder wholesale suppliers provide options for different industries, ensuring that manufacturers can choose the right gelling agent for each product’s unique needs.
Whether you’re looking for a versatile animal-based gelling agent like gelatin or premium collagen products, choosing the right supplier is essential. Funingpu’s reputation for quality and consistency has made it a trusted partner for B2B customers across industries and around the world.
FAQs
Q1: Pectin-isn't it the same as gelatin?
No, they are completely different. Pectin is a plant fiber that comes from fruits, while gelatin is an animal protein obtained from collagen.
Q2: Can gelatin take the place of the use of pectin?
Gelatin and pectin form different textures, the substitution of gelatin for pectin, or vice-versa, can also change the product's consistency. Need to be determined according to specific circumstances
Q3: What is the difference between gelatin powder versus pectin powder?
The former gives a smooth, melt-in-the-mouth texture, while pectin powder forms a firm and rigid gel. This textural change can be quite influential in changing the mouthfeel and look of the final product.
Phone: +86-577-88105990
Mobile: +86-138 5886 1938
Official Website: www.fnp-gelatin.com
Email: sales@funingpu.com
Address: No. 1-10 Wenpu Road, Yacheng Town, Xiapu County, Ningde City, Fujian Province




