-
July, 26,2025
Understanding the Role of Bloom Strength in Soft Gelatin Capsules
-
July, 25,2025
Bloom Strength and Its Impact on Hard Gelatin Capsules
-
July, 21,2025
How Gelatin Is Revolutionizing Pet Food: A Healthier Option for Dogs
-
June, 22,2025
Collagen as a Trusted Ingredient: Meeting Global Demand with Reliable Supply
Formulation of Soft Gelatin Capsules: A Pharma Expert Guide
Soft gelatin capsules—or softgels—stand as a cornerstone in pharmaceutical and nutraceutical delivery, offering unmatched versatility for drugs and supplements alike. From enhancing the bioavailability of poorly soluble APIs to delivering omega-3s with consumer-friendly ease, softgels owe their success to a formulation process perfected over decades, largely driven by gelatin’s unique properties. For pharmaceutical industry professionals and health product developers, understanding this process is key to unlocking innovative, reliable solutions that meet stringent regulatory and market demands.
As a leading gelatin manufacturer, we have witnessed how Funingpu gelatin shapes the softgel landscape, with its scalability, consistency, and adaptability making it the gold standard. Supporting a global supply chain that delivers billions of capsules annually, we provide the foundation for innovative, reliable solutions tailored to stringent regulatory and market demands.
This guide dives deep into the essentials: from core components and manufacturing processes to overcoming stability challenges and exploring cutting-edge trends. Tailored for pharma and nutraceutical experts, it blends practical insights with industry foresight—ensuring you’re equipped to formulate softgels that excel in performance and market appeal. Let’s explore why softgels, rooted in gelatin’s legacy, remain a vital tool for today’s formulators.

Understanding Soft Gelatin Capsules: Foundations and Importance
Soft gelatin capsules are more than a form of dosage; they are a delivery system weighing science and patient needs. To pharmaceutical and nutraceutical professionals, knowledge of their basis is the secret to unleashing their full potential. We here dissect their structure, importance, and enduring popularity in a competitive market.
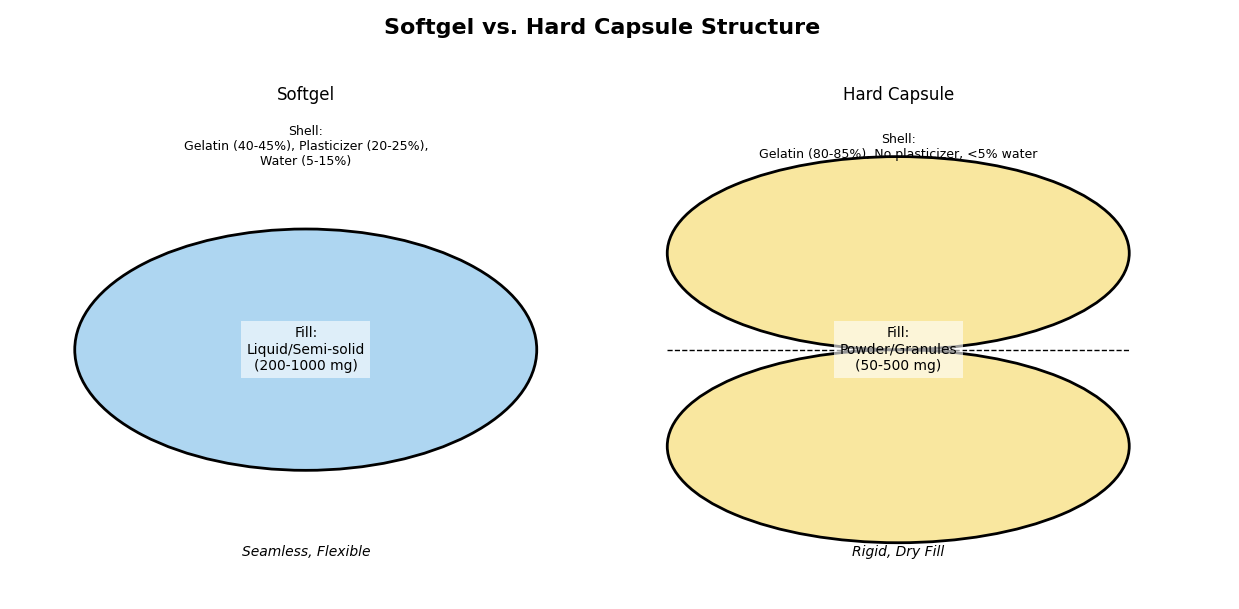
What Are Soft Gelatin Capsules?
Softgels consist of a gelatin-based, soft shell that contains a liquid or semi-solid fill. Compared to hard capsules, their leak-free structure—produced through processes like rotary die encapsulation—offers good leak resistance and flexibility. The shell's core is formed from gelatin made from collagen via controlled hydrolysis, combined with plasticizers (e.g., glycerol) and water to offer elasticity. The final formulation, refined by manufacturers over decades, offers a flexible yet robust capsule intended for numerous applications.
Why Softgels Matter in Pharma and Nutraceuticals
Softgels are better than tablets where they are needed. Their ability to solubilize lipophilic APIs to improve bioavailability is critical for BCS Class II/IV drugs like ibuprofen or fenofibrate. In nutraceuticals, they mask fish oil's taste and protect sensitive actives like vitamin E from oxidation. Patients also benefit: softgels are easy to swallow, enhancing compliance. From a production perspective, the consistency of gelatin—augmented by a scalable, high-quality manufacturing process—positions softgels as a first preference for quick development and stable manufacturing, a heritage that continues to drive adoption.

Market Demand and Industry Relevance
The softgel market thrives, fueled by growing demand for nutraceuticals (e.g., a $300 billion market by 2025) and precision pharmaceuticals. Gelatin is at the forefront—cost-effectiveness and established supply chain support billions of capsules every year. While plant-based alternatives are on the rise, gelatin-based softgels dominate, offering formulators a tried-and-true platform in evolving consumer and regulatory landscapes.
Core Components and Principles of Soft Gelatin Capsule Formulation
Formulating a soft gelatin capsule is a sensitive balance of science and skill, with each component being critically essential to performance and stability. For pharma and nutraceutical scientists, understanding these variables—especially the pivotal role of gelatin—is essential to developing successful products. This chapter explores shell and fill materials, important parameters, and practical applications, illustrating why gelatin remains at the heart of softgel success.
The Shell: Ingredients and Functions
The integrity of a softgel is established by the shell, and gelatin takes center stage. Derived from collagen through a gentle hydrolysis process, gelatin offers unmatched flexibility, strength, and solubility—qualities tuned by manufacturers to pharma-grade standards. Blended with plasticizers like glycerol or sorbitol (typically 20-30% by weight) and water (5-15%), it forms a flexible, durable casing. Gelatin's inherent film-forming nature, bolstered by an economical mass-producible manufacturing system, is batch-to-batch consistent whether it is a pilot scale for a small laboratory or manufacturing runs in commercial industry. What does it do? Encloses fills safely, protects actives, and degrades consistently in the body—enough reason to be the formulators' first choice anywhere.
Funingpu gelatin, derived from collagen through a meticulous hydrolysis process, offers unmatched flexibility, strength, and solubility—qualities honed by pharmaceutical gelatin suppliers like Funingpu to meet pharma-grade standards.

The Fill: Types and Compatibility
Inside the shell is the fill—liquid, semi-solid, or suspension—designated to the active ingredient. Oils (e.g., soybean oil or fish oil) dominate nutraceuticals, while suspensions or pastes suit pharmaceuticals like ibuprofen. Compatibility is of the essence: the fill must not degrade the gelatin shell, a challenge manufacturers address by subjecting it to severe testing. Lipophilic APIs work well in softgels, leveraging gelatin's hydrophobic barrier to enhance solubility. This synergy—fill and shell together—speaks to the versatility of gelatin, supporting vitamins up to sophisticated drugs.
Key Formulation Parameters
Success is also reliant on control of variables like viscosity, pH, and water content. Solutions of gelatin, typically 30-40% strength, require precise viscosity (e.g., 10,000-15,000 cP) for encapsulation—a process refined by the producers to permit reproducible shell thickness. Fill pH (ideally 4-7) must correlate with the stability range of the gelatin in order not to degrade it. Water content, precisely regulated at drying, controls shelf life—too high a level makes the product soft, too little creates brittleness. These values, refined over decades, testify to the flexibility of gelatin and the craftsmanship of manufacturing it.
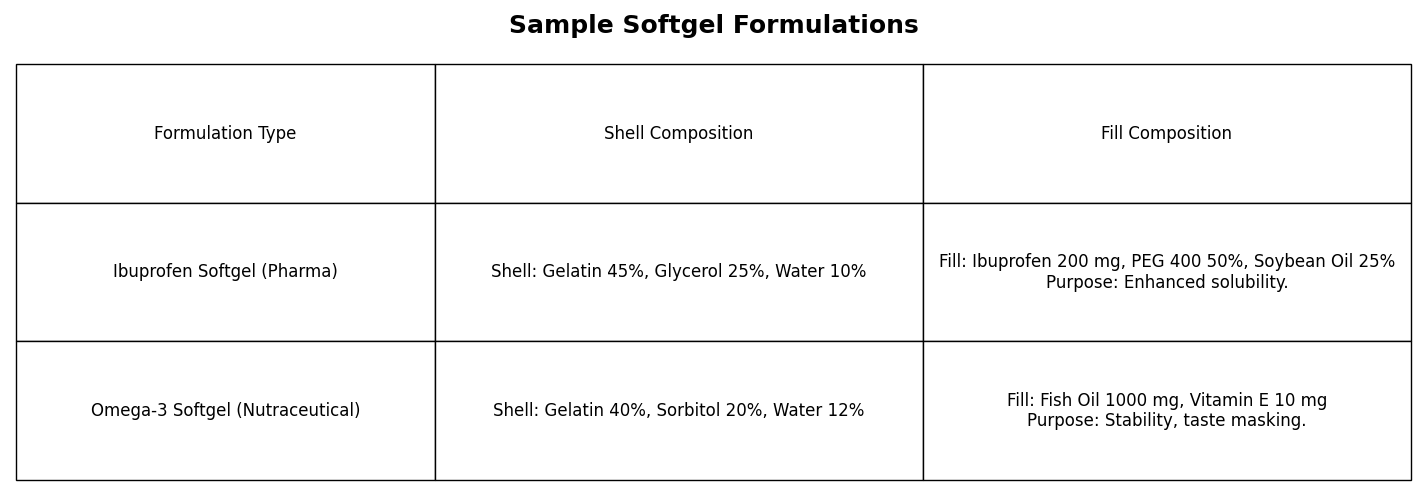
Sample Formulation Examples
To illustrate, consider two formulations:
- Pharma Example: Ibuprofen Softgel
- ·Shell: Gelatin (45%), glycerol (25%), water (10%).
- ·Fill: Ibuprofen (200 mg) in PEG 400 and soybean oil.
- ·Purpose: Boosts solubility for a BCS Class II drug.
- Nutraceutical Example: Omega-3 Softgel
- ·Shell: Gelatin (40%), sorbitol (20%), water (12%).
- ·Fill: Fish oil (1000 mg) with vitamin E (antioxidant).
- ·Purpose: Masks taste, protects against oxidation.
These examples showcase gelatin’s role in enabling scalable, effective softgels, a testament to its manufacturing precision.
The Softgel Manufacturing Process: From Lab to Production
Converting a formula to a complete soft gelatin capsule requires precision, expertise, and a process refined over decades—skills gelatin manufacturers bring to the table. Rotary die encapsulation, the standard method, forms gelatin and fill material into smooth softgels suitable for pharma and nutraceutical applications. Here, the process is broken down, key controls, and scaling factors, recognizing how gelatin's uniformity powers production success from lab to shelf.
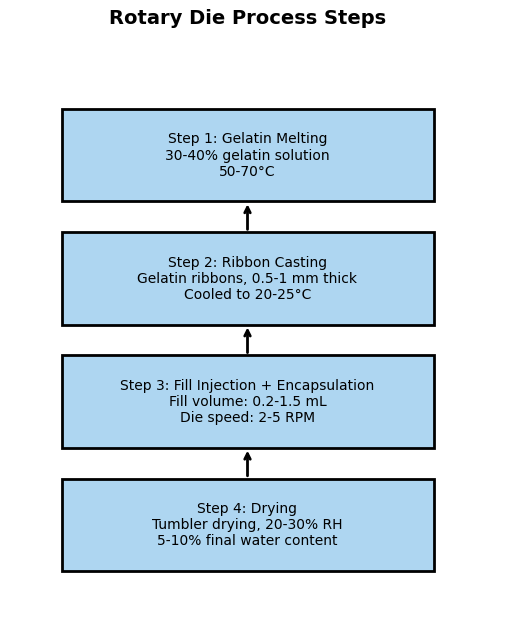
Overview of the Rotary Die Process
It begins with two parallel steps: filling and preparation of the gelatin shell. Melted gelatin as a viscous solution (30-40% concentration) along with plasticizers like glycerol is filled in thin strips onto cold drums—a process that is perfected by the manufacturers to uniformity. The fill (nutraceutical blend or oil soluble API) is filled simultaneously into a reservoir. These ribbons are fed into the rotary die machine where two registering dies with pockets cut and seal the gelatin over the filled-in fill to form capsules. Following encapsulation, softgels are tumbling-dried to reduce water content to 5-10%. This productive process, using gelatin's film-forming capacity, forms leak-proof uniform softgels every time.
Critical Process Controls
Close control is required for quality. Temperature (melting the gelatin at 50-70°C) needs to be precise—too much can break it down, too little prevents flow. Humidity in drying (20-30% RH) prevents stickiness or cracking, a balance gelatin's natural toughness enables. Timing is as important as well: too much drying embrittles the shell, too little reduces shelf life. Plants use decades of know-how to dial in these conditions so gelatin's attributes—scale and reproducibility—are translated into high yields and regulatory approval, be it for small batches or mass production.
Scaling Up: Lab to Industrial Considerations
Scaling up from industrial to lab level adds value to gelatin. In the laboratory, small rotary die units test formulations, relying on gelatin's consistency for quick iteration. Industrial production demands larger machines (e.g., 100,000 capsules/hour), where the strength of a pharmaceutical gelatin manufacturer like Funingpu shines. Our established supply chain—delivering billions of kilos annually—keeps costs low compared to alternatives, ensuring batch uniformity and rapid market entry. Cost-effectiveness is also key: gelatin's established manufacturing process keeps costs low against newcomer alternatives. Such issues as batch-to-batch consistency or equipment wear are surmounted by gelatin's proven track record, and thus it is the foundation of the pharma and nutraceutical industry softgel scalability.
Overcoming Common Formulation Challenges
Even with gelatin’s proven strengths, softgel formulation isn’t without hurdles. Pharmaceutical and nutraceutical experts face challenges like shell crosslinking, fill interactions, and stability concerns—issues that can derail product quality if unchecked. As gelatin manufacturers, we’ve refined processes and solutions to tackle these head-on, ensuring softgels meet rigorous standards. This section explores these challenges and offers practical strategies, underscoring gelatin’s adaptability as a trusted foundation.
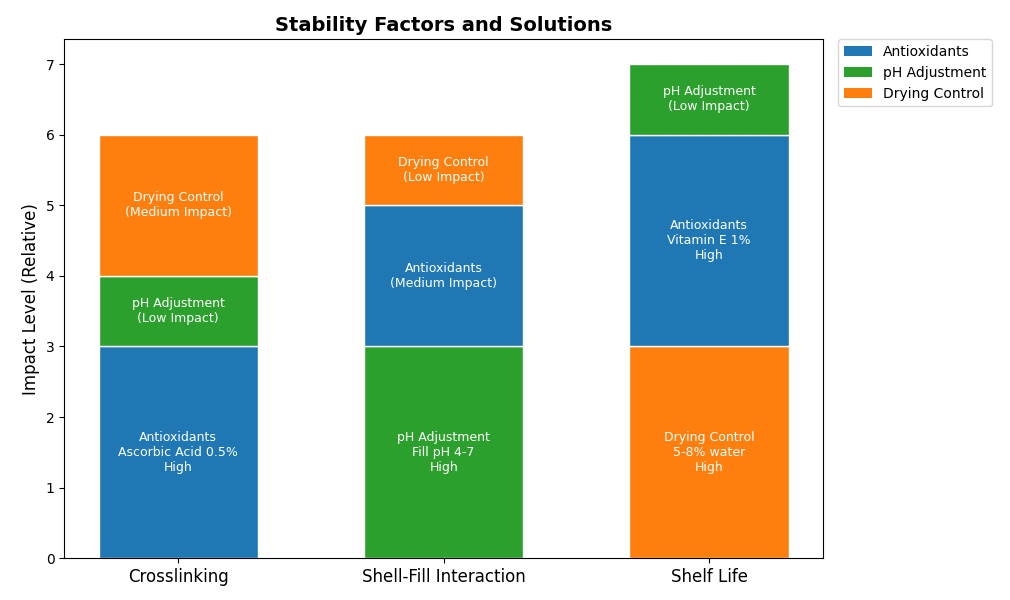
Crosslinking of Gelatin Shells
Crosslinking—a chemical process that stiffens the gelatin shell—can slow dissolution, compromising drug release. It's typically caused by aldehydes (from fill ingredients or oxidation) or high humidity storage. While Article 3 covers this issue, gelatin's strength comes through solutions: manufacturers recommend avoiding aldehyde-producing excipients (e.g., certain flavorings) and adding antioxidants like ascorbic acid to the fill. Pre-formulation testing, pioneered in the production of gelatin, identifies risks in advance. With appropriate controls, gelatin softgels continue to enjoy dissolution superiority, proven after decades.
Shell-Fill Interactions
Fill-gelatin shell contact can compromise stability—water migrating into shells makes them soft, but reactive APIs like acids weaken gelatin. This is a challenge with complex fills like high-strength medicines or essential oils. Solutions take advantage of gelatin's manufacturing precision: adjust fill pH to 4-7 (stable gelatin range), use hydrophobic barriers like lecithin, or adjust shell water content (e.g., 8-10%). Solutions, backed by gelatin's consistent quality, offer compatibility, keeping softgels intact from production to patient.
Stability and Shelf-Life Optimization
Shelf life is a battle against water, heat, and oxidation. Over 10% water in the shell jeopardizes microbial growth; heat softens gelatin; oxygen rancidifies fats like omega-3s. Gelatin manufacturers counterattack with drying precision (targeting 5-8% residual water) and robust packaging—foil blisters or nitrogen-flushed bottles. Adding antioxidants (e.g., tocopherol) to fill, an optimized process with the gelatin's supply chain, increases stability. These processes highlight gelatin's role in providing softgels that endure, even in challenging conditions.
Troubleshooting Tips for Formulators
During times of crisis, quick fixes are essential. Soft shells? Increase gelatin strength (e.g., 45%) or drying time. Leaking capsules? Check fill viscosity (aim for 500-1000 cP) and seal integrity—areas where gelatin consistency is aided by uniformity. Brittleness? Adjust plasticizer ratios (e.g., 25% glycerol). These manufacturing tips, learned from experience, allow formulators to make softgel adjustments, leveraging gelatin's tolerance to repair issues without losing batches.
Innovations and Trends in Soft Gelatin Capsule Formulation
The softgel environment is evolving, with innovative materials and sustainability goals paving new ways. For pharma and nutraceutical professionals, staying ahead means seeing these changes—although, as gelatin manufacturers, Funingpu sees gelatin's heritage as a vital anchor during change. Its proven track record, honed through decades of production expertise, still meets today's demands. This part addresses plant alternatives, green innovations, and future directions, bringing innovation into balance with gelatin's unrivaled heritage.
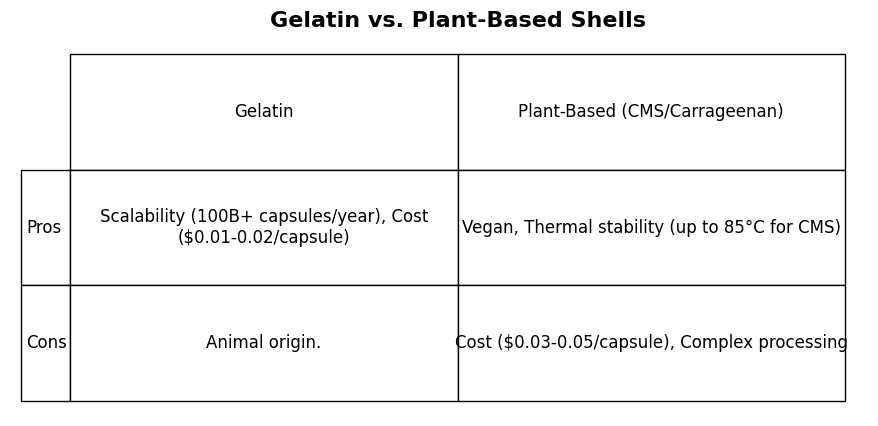
Gelatin Alternatives: The Rise of Plant-Based Softgels
Plant-based softgels, e.g., those using carboxymethyl starch (CMS) or carrageenan, have been driven by vegan and thermal stability demands. CMS achieves high phase-transition temperatures (up to 85°C), and carrageenan is suitable for dietary restrictions. These alternatives find niche markets—yet gelatin, derived from collagen via a streamlined hydrolysis process, remains the benchmark. Its scalability, cost savings, and consistent quality are outpacing plants' complex processing and higher cost. With increasing alternatives, the maturity of gelatin's production means it is meeting most formulation needs with ease.
Sustainability in Softgel Production
Sustainability is revolutionizing softgel manufacturing, from supply to waste minimization. Gelatin manufacturers like Funingpu are leading the way here again—collagen from the by-products of the meat industry is circular economy aligned, with very little environmental impact. Attempts to diminish water use in gelatin production (e.g., effective drying) and make packaging recyclable further decrease the footprint. Plant-based substitutes, while eco-friendly-sounding, will often involve energy-intensive synthesis to temper their advantage. Gelatin's established production chain, producing billions of capsules per year, presents a sustainable base that's hard to beat.
Advanced Applications and Future Directions
Forward to 2025 and beyond, softgels change. Enteric-coated gelatin softgels target drug delivery, ideal for acid-sensitive APIs. Non-animal trends persist, but gelatin changes—blends with stabilizers provide improved performance without abandoning its roots. Advances like microencapsulated fills or chewable softgels expand gelatin's utility in nutraceuticals. Experience on the part of manufacturers allows these innovations to scale well, cementing gelatin as a versatile platform. Plant-based softgels gain traction, but gelatin's versatility keeps it as a leading edge formulation innovator.
Real-World Applications: Case Studies and Insights
Soft gelatin capsules excel in practice, delivering solutions for complex pharmaceutical and nutraceutical needs. As gelatin manufacturers, Funingpu has seen how gelatin’s reliability—rooted in a robust production process—turns formulation challenges into market successes. This section presents two case studies—one pharma, one nutraceutical—illustrating gelatin’s versatility, alongside key takeaways for formulators. These real-world examples highlight why gelatin remains a cornerstone for industry experts.
Pharmaceutical Case Study: Enhancing Poorly Soluble Drugs
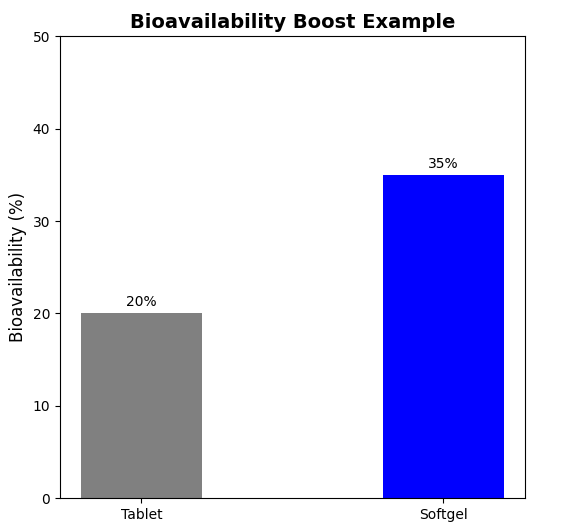
Consider the case of fenofibrate, a BCS Class II drug with poor solubility. A softgel formulation increases its bioavailability, capitalizing on the advantages of gelatin. The shell—45% gelatin, 25% glycerol, 10% water—encloses a fill of fenofibrate (145 mg) in a mixture of soybean oil and PEG 400. Gelatin's hydrophobic barrier breaks down the API, and its leak-proof encapsulation, fine-tuned by manufacturers, prevents leakage. Clinical results are a 35% bioavailability gain over tablets because of gelatin's consistent quality at any production level. This illustrates gelatin's benefit for solubility in a solution—a pharma milestone.
Nutraceutical Case Study: Optimizing Omega-3 Delivery
Omega-3 softgels dominate supplements, and gelatin makes them shine. A typical formula uses a 40% gelatin, 20% sorbitol, and 12% water shell containing 1000 mg fish oil and supplemental vitamin E (10 mg) as an antioxidant. Gelatin's manufacturing precision hides fishy odors and inhibits oxidation, ensuring consumer acceptability and stability. Drying to 6% residual water—a process gelatin manufacturers maximize—increases shelf life to two years. This formulation, replicated to millions of units per year, highlights gelatin's cost-savviness and dependability for nutraceutical giants.
Lessons Learned for Developers
These cases offer insights:
- ·Solubility: Gelatin softgels excel for lipophilic actives—test fill blends early.
- ·Stability: Antioxidants and tight drying controls, backed by gelatin’s uniformity, are key.
- ·Scalability: Gelatin’s supply chain supports rapid market entry, from pilot to production.
Formulators benefit from gelatin’s adaptability, honed by manufacturers, to meet diverse needs without compromising quality.
Final Thoughts
Soft gelatin capsules remain a powerhouse in pharmaceutical and nutraceutical delivery, blending science, practicality, and market appeal. From their core components—where gelatin’s versatility shines—to the precision of the rotary die process, softgels showcase a formulation art perfected over decades. As gelatin manufacturers, Funingpu has highlighted how this collagen-derived material, backed by a scalable, quality-assured production system, overcomes challenges like crosslinking and stability, delivering reliable solutions for drugs like fenofibrate and supplements like omega-3s. Its adaptability ensures it meets today’s needs while supporting tomorrow’s innovations.
The trends are clear: plant-based softgels and sustainability matter, yet gelatin’s cost-effectiveness, consistency, and proven performance keep it at the forefront. Whether enhancing bioavailability or scaling production, gelatin softgels offer pharma and nutraceutical experts a trusted platform to innovate with confidence. Our case studies prove it—gelatin’s manufacturing legacy turns formulation hurdles into competitive advantages.
Looking ahead, softgel formulation will evolve, but gelatin’s foundation endures. For formulators, the message is simple: leverage its strengths, test creatively, and trust in a material that’s stood the test of time. Have insights or challenges from your softgel projects? Share them below or explore our resources—let’s keep pushing the boundaries of what softgels can achieve.
Phone: +86-577-88105990
Mobile: +86-138 5886 1938
Official Website: www.fnp-gelatin.com
Email: sales@funingpu.com
Address: No. 1-10 Wenpu Road, Yacheng Town, Xiapu County, Ningde City, Fujian Province




